Are you ready to safeguard sensitive healthcare data and earn the trust of today’s healthcare industry? Becoming HIPAA compliant is not just a choice—it’s a necessity.
HIPAA stands for Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act. It is a piece of law designed to ensure the security and confidentiality of patient health information.
With data breaches and cyber threats on the rise, HIPAA compliance is not just a best practice but a legal requirement.
HIPAA compliance requires healthcare organizations of all sizes to follow a detailed set of rules and regulations. Interestingly, 95% of early-stage startups are unprepared to meet enterprise security requirements.
Read on as we outline the key steps to help you navigate the intricate path to HIPAA compliance, ensuring your organization is not only in compliance with the law but also actively protecting patient and industry trust.
Understanding HIPAA Requirements
HIPAA regulations include three main components:
- Privacy Rule: protects patients’ health information
- Security Rule: ensures the security of digital health data
- Breach Notification Rule: makes sure you report any data breaches promptly
HIPAA doesn’t just affect healthcare providers; it applies to covered entities like health plans, insurance companies, and healthcare clearinghouses responsible for processing health information.
Here are three key reasons for adhering to HIPAA’s regulations:
- Penalty Costs: Non-compliance with regulations can result in hefty penalties. Fines can range from $100 to $1.5 million, and there’s the potential for criminal charges with jail time (in case of intentional violations). Patients may have the right to sue for damages if their privacy is breached.
- Patient Confidentiality: Complying with HIPAA standards represents an organization’s commitment to preserving the confidentiality of patient data.
- Establishing Industry Trust: The healthcare sector is built on mutual trust and the shared goal of patient well-being. When an organization invests time and resources into understanding and implementing HIPAA regulations, it sends a clear message to peers, partners, and patients alike: “We prioritize safety, privacy, and excellence.”
Conducting a HIPAA Compliance Gap Analysis
Conducting a gap analysis is an important step in your HIPAA compliance journey. It helps you to assess where you currently stand and what steps might be outstanding in order for your organization to meet HIPAA requirements.
To evaluate your practices against HIPAA rules, do the following:
- Gather HIPAA Materials: Collect all your HIPAA-related documents, such as policies, procedures, and training materials.
- Identify Applicable Requirements: See which specific HIPAA rules apply to your organization based on its type and size.
- Create a Checklist: Make a checklist of HIPAA requirements that cover patient privacy, data security, and breach response.
- Assess Your Current Practices: Compare your existing practices with the checklist. Pinpoint gaps or areas where you need to meet the requirements.
- Document Your Findings: Clearly document the gaps you’ve identified, detailing what needs improvement.
- Develop an Action Plan: To address these gaps, assign responsibilities and set deadlines for necessary changes.
- Implement the Changes: Put your action plan into motion. Update policies and procedures, ensure staff is trained, and enhance security measures.
- Monitor and Review: Continually review your HIPAA compliance efforts. Make adjustments as needed to maintain ongoing compliance.
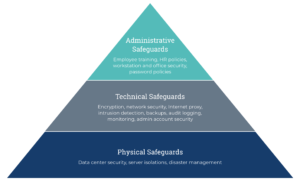
How to Implement HIPAA Technical Safeguards
HIPAA technical safeguards are vital for your data security. Two key technical safeguards to focus on are access controls and encryption.
Access Controls
You must be aware that only authorized people can access sensitive health information. Create unique usernames and passwords, set up user permissions so each person only sees what they need, and regularly review who has access to adjust as needed.
Encryption
You also need to encrypt data to protect it during transmission and storage. Encryption scrambles data into a code that only authorized users can read. Use secure protocols for emails and data sharing. Encrypt laptops, smartphones, and any devices that store patient info.
Regularly updating and maintaining these security measures is essential. Here’s why:
- Become More Resistant to Threats: Cyber threats are always changing. Regular updates help your security keep pace with new dangers.
- Fix Vulnerabilities: Updates often include patches to fix security holes. Without updates, you’re vulnerable.
- Stay Compliant: HIPAA expects you to adapt to new threats. Non-compliance can lead to hefty penalties.
- Protect Patient Trust: Patients trust you with their data. Regular security maintenance shows you take their privacy seriously.
How to Become HIPAA-Compliant By Establishing Physical Safeguards
Physical safeguards are essential to protect healthcare facilities and equipment. They prevent unauthorized access and theft of sensitive patient data.
Access controls keep a close check that only authorized personnel enter secure areas. Facility security, like cameras and alarms, deters potential threats and helps catch security breaches.
Workstation policies keep computers and data secure from tampering or theft. Without these safeguards, patient information could be exposed, leading to privacy breaches and legal issues.
Physical safeguards also ensure the safety of patients and staff in emergencies, like fires or disasters. Here are the top eight physical safeguards you can implement:
- Access Controls: You must restrict who can enter certain areas. Use locks, badges, and keycards to limit access to authorized personnel only. This prevents unauthorized people from wandering into sensitive areas.
- Facility Security: Installing surveillance cameras in hallways, entrances, and critical areas can deter potential threats. These cameras also help in identifying any security breaches. Check that exterior doors and windows are sturdy and can’t be easily tampered with.
- Workstation Policies: Keep computers and other electronic devices containing patient data in secure areas. Lock them when not in use. Set some policies that require employees to log out of their workstations when they step away.
- Alarm Systems: Set up alarm systems that alert security or staff in case of unauthorized access or security breaches. These alarms can be connected to doors, windows, and critical equipment.
- Visitor Verification: When visitors arrive, have a system to verify their identity and purpose for being in the facility. Visitors should be accompanied or monitored, especially in sensitive areas.
- Emergency Preparedness: Plan for emergencies like fires, natural disasters, or medical emergencies. Have evacuation routes and supplies readily available to ensure everyone’s safety.
- Inventory Management: Keep a record of all medical equipment and supplies. Regularly audit your inventory to prevent theft or loss.
- Secure Data Storage: Patient records and sensitive information must be stored securely, either electronically with encryption or in locked cabinets. Limit access to this information to authorized personnel only.
Ensuring HIPAA Administrative Compliance
Administrative safeguards play a crucial role in becoming HIPAA compliant. These safeguards are like the captain steering the ship to keep sensitive health information safe.
Policies serve as your rulebook, providing clear guidelines and expectations for handling sensitive health information. Think of them as the compass that guides you safely through HIPAA’s regulatory requirements.
Similarly, procedures are like step-by-step instructions for operating everything. They tell your staff how to handle patient data correctly, ensuring each member knows their role and responsibilities.
Employee training is also a necessity to ensure your staff understands and adheres to HIPAA regulations.
Training provides your team with the necessary knowledge to perform their roles effectively within the framework of HIPAA.
You should also designate a Compliance Officer responsible for overseeing HIPAA compliance efforts within your organization.
Finally, a well-defined incident response plan is crucial in the event of a security incident or breach. This plan outlines the steps to take if an incident occurs, helping to minimize the impact and ensure a swift and appropriate response.
How to Conduct Regular HIPAA Risk Assessments and Audits
These evaluations play an important ongoing role in safeguarding sensitive healthcare information.
Regular risk assessments and audits are essential because they help you identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities in your healthcare organization’s data security.
You can proactively address emerging threats by continuously monitoring and evaluating your systems.
1. Build Your Compliance Team
Start by assembling your compliance team. You need individuals who are well-versed in HIPAA regulations to oversee this critical process. This can be an in-house team or an external partner such as MedStack.
2. Identify PHI Storage Areas
Pinpoint every nook and cranny in your organization where protected health information (PHI) is stored or processed. This includes electronic health records, physical files, and any other storage methods.
3. Assess Risks Thoroughly
Dig deep and assess the risks associated with each PHI storage area. Leave no stone unturned. Consider the chances of various security breaches and vulnerabilities.
4. Implement Security Measures
Implement security measures to address any known risks. This includes measures such as encryption, access controls, and keeping all software up to date. Keep detailed records of all the changes you make.
5. Regular Audits are Key
Conduct regular internal and external audits (at least annually) to assess your processes, policies, and security mechanisms.
Consider the following key areas during your audit process:
- Ensure only authorized individuals can access PHI.
- Confirm that stored and transmitted data is encrypted.
- Identify potential vulnerabilities and address them proactively.
- Test the effectiveness of your response to security breaches.
- Check the protection of servers, computers, and other hardware.
- Ensure staff training on privacy and security is up-to-date.
- Confirm that backups are regular, secure, and retrievable.
6. Document Findings and Create a Plan
After an audit has been completed, document your findings and create an action plan. This might involve further enhancing security measures, updating policies, or providing additional employee training.
Responding to Security Incidents and Breaches
When an incident like a data breach or a cyber attack occurs, it’s important to report it immediately to ensure everyone is informed. Here’s why:
Reporting incidents quickly helps to stop more data leaks from happening. The longer you wait, the worse it can get.
In addition, many laws dictate a specific timeframe for reporting disclosures.
Here’s how to proceed if such events occur:
- Identify the Incident: Start by recognizing that an incident has occurred. This could be unusual network activity, unauthorized access, or suspicious behavior. Early detection is paramount!
- Contain the Incident: Isolate the affected systems or networks to prevent further damage. Disconnect compromised devices from the internet and other networked resources.
- Assess the Impact: See the extent of the breach to understand what data or systems are compromised. This helps in prioritizing your response efforts.
- Engage Your Incident Response Team: Activate your incident response team, including IT experts, legal counsel, and communication specialists. Define roles and responsibilities clearly.
- Preserve Evidence: Avoid tampering with the evidence, as it may be needed for investigations or legal proceedings. Make backups and snapshots of affected systems.
- Notify Relevant Authorities: If the law requires, report the breach to regulatory and law enforcement agencies. Compliance with data protection laws is essential.
- Notify Affected Parties: Inform customers, employees, and other affected parties about the breach promptly. Be transparent about what happened, what data was compromised, and what you’re doing to address it.
- Contain the Damage: Work on fixing the vulnerabilities that led to the breach. This may involve patching software, changing passwords, or enhancing security measures.
- Investigate the Incident: Conduct a thorough investigation to determine the breach’s root cause and assess the damage’s scope. This helps in preventing future incidents.
- Review and Update Security Policies: Learn from the incident and improve your security policies and procedures. Implement necessary changes to prevent similar breaches in the future.
Final Thoughts
HIPAA compliance can often feel overwhelming. Every slip-up could lead to hefty fines and damaged trust.
Imagine a streamlined process where every compliance box is ticked off with confidence.
That’s where MedStack comes in. Click here to explore our trusted HIPAA Compliance Software and ensure your organization remains compliant and secure.